这几个高级前端常用的API,你用到了吗?
作者:lzg9527
来源:SegmentFault 思否社区
MutationObserver
MutationObserver 是一个可以监听 DOM 结构变化的接口。当 DOM 对象树发生任何变动时,MutationObserver 会得到通知。
API
MutationObserver 是一个构造器,接受一个 callback 参数,用来处理节点变化的回调函数,返回两个参数:
mutations:节点变化记录列表(sequence<MutationRecord>) observer:构造 MutationObserver 对象。
observe:设置观察目标,接受两个参数,target:观察目标,options:通过对象成员来设置观察选项。 disconnect:阻止观察者观察任何改变。 takeRecords:清空记录队列并返回里面的内容。
//选择一个需要观察的节点
var targetNode = document.getElementById('root')
// 设置observer的配置选项
var config = { attributes: true, childList: true, subtree: true }
// 当节点发生变化时的需要执行的函数
var callback = function (mutationsList, observer) {
for (var mutation of mutationsList) {
if (mutation.type == 'childList') {
console.log('A child node has been added or removed.')
} else if (mutation.type == 'attributes') {
console.log('The ' + mutation.attributeName + ' attribute was modified.')
}
}
}
// 创建一个observer示例与回调函数相关联
var observer = new MutationObserver(callback)
//使用配置文件对目标节点进行观测
observer.observe(targetNode, config)
// 停止观测
observer.disconnect()
childList:设置 true,表示观察目标子节点的变化,比如添加或者删除目标子节点,不包括修改子节点以及子节点后代的变化。
attributes:设置 true,表示观察目标属性的改变。
characterData:设置 true,表示观察目标数据的改变。
subtree:设置为 true,目标以及目标的后代改变都会观察。
attributeOldValue:如果属性为 true 或者省略,则相当于设置为 true,表示需要记录改变前的目标属性值,设置了 attributeOldValue 可以省略 attributes 设置。
characterDataOldValue:如果 characterData 为 true 或省略,则相当于设置为 true,表示需要记录改变之前的目标数据,设置了 characterDataOldValue 可以省略 characterData 设置。
特点
它等待所有脚本任务完成后才会运行,即采用异步方式。 它把 DOM 变动记录封装成一个数组进行处理,而不是一条条地个别处理 DOM 变动。 它即可以观察发生在 DOM 节点的所有变动,也可以观察某一类变动。
IntersectionObserver
API
var io = new IntersectionObserver(callback, option)
// 开始观察
io.observe(document.getElementById('example'))
// 停止观察
io.unobserve(element)
// 关闭观察器
io.disconnect()
io.observe(elementA)
io.observe(elementB)
var io = new IntersectionObserver((entries) => {
console.log(entries)
})
time:可见性发生变化的时间,是一个高精度时间戳,单位为毫秒。 target:被观察的目标元素,是一个 DOM 节点对象。 isIntersecting: 目标是否可见。 rootBounds:根元素的矩形区域的信息,getBoundingClientRect()方法的返回值,如果没有根元素(即直接相对于视口滚动),则返回 null。 boundingClientRect:目标元素的矩形区域的信息。 intersectionRect:目标元素与视口(或根元素)的交叉区域的信息。 intersectionRatio:目标元素的可见比例,即 intersectionRect 占 boundingClientRect 的比例,完全可见时为 1,完全不可见时小于等于 0
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#div1 {
position: sticky;
top: 0;
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
text-align: center;
background: black;
color: #ffffff;
font-size: 18px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">首页</div>
<div style="height: 1000px;"></div>
<div id="div2" style="height: 100px; background: red;"></div>
<script>
var div2 = document.getElementById('div2')
let observer = new IntersectionObserver(
function (entries) {
entries.forEach(function (element, index) {
console.log(element)
if (element.isIntersecting) {
div1.innerText = '我出来了'
} else {
div1.innerText = '首页'
}
})
},
{
root: null,
threshold: [0, 1]
}
)
observer.observe(div2)
</script>
</body>
</html>

图片懒加载
const imgs = document.querySelectorAll('img[data-src]')
const config = {
rootMargin: '0px',
threshold: 0
}
let observer = new IntersectionObserver((entries, self) => {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
if (entry.isIntersecting) {
let img = entry.target
let src = img.dataset.src
if (src) {
img.src = src
img.removeAttribute('data-src')
}
// 解除观察
self.unobserve(entry.target)
}
})
}, config)
imgs.forEach((image) => {
observer.observe(image)
})
无限滚动
var intersectionObserver = new IntersectionObserver(function (entries) {
// 如果不可见,就返回
if (entries[0].intersectionRatio <= 0) return
loadItems(10)
console.log('Loaded new items')
})
// 开始观察
intersectionObserver.observe(document.querySelector('.scrollerFooter'))
getComputedStyle()
API
document.defaultView.getComputedStyle(element[,pseudo-element])
// or
window.getComputedStyle(element[,pseudo-element])
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
#myDiv {
background-color: blue;
width: 100px;
height: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="myDiv" style="background-color: red; border: 1px solid black"></div>
</body>
<script>
function getStyleByAttr(obj, name) {
return window.getComputedStyle ? window.getComputedStyle(obj, null)[name] : obj.currentStyle[name]
}
let node = document.getElementById('myDiv')
console.log(getStyleByAttr(node, 'backgroundColor'))
console.log(getStyleByAttr(node, 'width'))
console.log(getStyleByAttr(node, 'height'))
console.log(getStyleByAttr(node, 'border'))
</script>
</html>
和 style 的异同
element.style 读取的只是元素的内联样式,即写在元素的 style 属性上的样式;而 getComputedStyle 读取的样式是最终样式,包括了内联样式、嵌入样式和外部样式。 element.style 既支持读也支持写,我们通过 element.style 即可改写元素的样式。而 getComputedStyle 仅支持读并不支持写入。我们可以通过使用 getComputedStyle 读取样式,通过 element.style 修改样式。
getBoundingClientRect
API
let DOMRect = object.getBoundingClientRect()
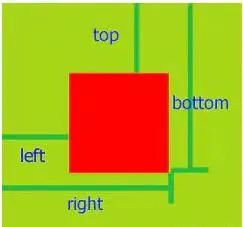
应用场景
// 获取dom元素相对于网页左上角定位的距离
function offset(el) {
var top = 0
var left = 0
do {
top += el.offsetTop
left += el.offsetLeft
} while ((el = el.offsetParent)) // 存在兼容性问题,需要兼容
return {
top: top,
left: left
}
}
var odiv = document.getElementsByClassName('markdown-body')
offset(a[0]) // {top: 271, left: 136}
var positionX = this.getBoundingClientRect().left + document.documentElement.scrollLeft
var positionY = this.getBoundingClientRect().top + document.documentElement.scrollTop
function isElView(el) {
var top = el.getBoundingClientRect().top // 元素顶端到可见区域顶端的距离
var bottom = el.getBoundingClientRect().bottom // 元素底部端到可见区域顶端的距离
var se = document.documentElement.clientHeight // 浏览器可见区域高度。
if (top < se && bottom > 0) {
return true
} else if (top >= se || bottom <= 0) {
// 不可见
}
return false
}
requestAnimationFrame
API
window.requestAnimationFrame(callback)
window._requestAnimationFrame = (function () {
return (
window.requestAnimationFrame ||
window.webkitRequestAnimationFrame ||
window.mozRequestAnimationFrame ||
function (callback) {
window.setTimeout(callback, 1000 / 60)
}
)
})()
var globalID
function animate() {
// done(); 一直运行
globalID = requestAnimationFrame(animate) // Do something animate
}
globalID = requestAnimationFrame(animate) //开始
cancelAnimationFrame(globalID) //结束
var progress = 0
//回调函数
function render() {
progress += 1 //修改图像的位置
if (progress < 100) {
//在动画没有结束前,递归渲染
window.requestAnimationFrame(render)
}
}
//第一帧渲染
window.requestAnimationFrame(render)
优点:
CPU 节能:使用 setTimeout 实现的动画,当页面被隐藏或最小化时,setTimeout 仍然在后台执行动画任务,由于此时页面处于不可见或不可用状态,刷新动画是没有意义的,完全是浪费 CPU 资源。而 requestAnimationFrame 则完全不同,当页面处理未激活的状态下,该页面的屏幕刷新任务也会被系统暂停,因此跟着系统步伐走的 requestAnimationFrame 也会停止渲染,当页面被激活时,动画就从上次停留的地方继续执行,有效节省了 CPU 开销。 函数节流:在高频率事件(resize,scroll 等)中,为了防止在一个刷新间隔内发生多次函数执行,使用 requestAnimationFrame 可保证每个刷新间隔内,函数只被执行一次,这样既能保证流畅性,也能更好的节省函数执行的开销。一个刷新间隔内函数执行多次时没有意义的,因为显示器每 16.7ms 刷新一次,多次绘制并不会在屏幕上体现出来。
应用场景
$(window).on('scroll', function () {
window.requestAnimationFrame(scrollHandler)
})
const scrollToTop = () => {
const c = document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop
if (c > 0) {
window.requestAnimationFrame(scrollToTop)
window.scrollTo(0, c - c / 8)
}
}
scrollToTop()
//需要插入的容器
let ul = document.getElementById('container')
// 插入十万条数据
let total = 100000
// 一次插入 20 条
let once = 20
//总页数
let page = total / once
//每条记录的索引
let index = 0
//循环加载数据
function loop(curTotal, curIndex) {
if (curTotal <= 0) {
return false
}
//每页多少条
let pageCount = Math.min(curTotal, once)
setTimeout(() => {
for (let i = 0; i < pageCount; i++) {
let li = document.createElement('li')
li.innerText = curIndex + i + ' : ' + ~~(Math.random() * total)
ul.appendChild(li)
}
loop(curTotal - pageCount, curIndex + pageCount)
}, 0)
}
loop(total, index)
//需要插入的容器
let ul = document.getElementById('container')
// 插入十万条数据
let total = 100000
// 一次插入 20 条
let once = 20
//总页数
let page = total / once
//每条记录的索引
let index = 0
//循环加载数据
function loop(curTotal, curIndex) {
if (curTotal <= 0) {
return false
}
//每页多少条
let pageCount = Math.min(curTotal, once)
window.requestAnimationFrame(function () {
for (let i = 0; i < pageCount; i++) {
let li = document.createElement('li')
li.innerText = curIndex + i + ' : ' + ~~(Math.random() * total)
ul.appendChild(li)
}
loop(curTotal - pageCount, curIndex + pageCount)
})
}
loop(total, index)
监控卡顿方法
var lastTime = performance.now()
var frame = 0
var lastFameTime = performance.now()
var loop = function (time) {
var now = performance.now()
var fs = now - lastFameTime
lastFameTime = now
var fps = Math.round(1000 / fs)
frame++
if (now > 1000 + lastTime) {
var fps = Math.round((frame * 1000) / (now - lastTime))
frame = 0
lastTime = now
}
window.requestAnimationFrame(loop)
}


关注公众号:拾黑(shiheibook)了解更多
赞助链接:
关注数据与安全,洞悉企业级服务市场:https://www.ijiandao.com/
四季很好,只要有你,文娱排行榜:https://www.yaopaiming.com/
让资讯触达的更精准有趣:https://www.0xu.cn/
 关注网络尖刀微信公众号
关注网络尖刀微信公众号随时掌握互联网精彩








 微信扫码关注公众号
微信扫码关注公众号